
Gravitational lenses
In astronomy, for some time, the phenomenon of lens effects is known and they are attributed to the gravity of massive celestial objects such as galaxies and galaxy clusters. According to this model, the light is similar to a lens, is distracted of massive celestial objects and this may lead to multiple images. By the deflection of light beams an amplification attenuation, and distortion of the observed celestial objects takes place.
Figure 1: Gravitational lens - basic representation
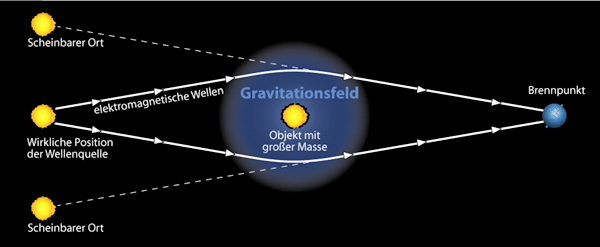
Source: http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitationslinseneffekt
Figure 2: A typical Gravitational lens effect. Galaxies in wide distances appear as circular sections
Figure 2: A typical Gravitational lens effect. Galaxies in wide distances appear as circular sections
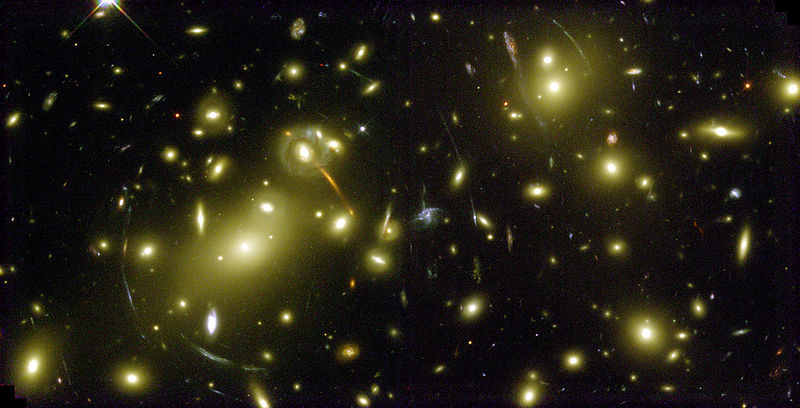

Source: http://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gravitationslinseneffekt
Figure 3: Galaxy cluster Cl0024+17, taken by Hubble-Space telescope.
Figure 3: Galaxy cluster Cl0024+17, taken by Hubble-Space telescope.
Download this article as PDF-File .
An optical analysis of voids lens effects
Theory of everything
3. An alternative Explanation of lens effects
The understanding of the causes of lens effects has far-reaching consequences for astronomy. With our telescopes we see the universe through different sized "hollow glass spheres," which consist of differently sized voids. As a kind of "cosmic censorship" we therefore cannot achieve a look into the distant regions of the universe.
On my website, you can see pictures of telescopes that I have optically analyzed with the help of a simple drawing program. I will first summarize my analysis results briefly below. When viewing the telescope images, the following arguments can be better understood.
There are no gravitational lenses but only voids lenses
The amplification, attenuation, and distortion of the astronomical images, which takes place through the deflection of light beams so far has been explained as a result of gravity. It is the ordinary optical properties of light in the transition to another medium. For the explanation of astronomical lenses you do not need the effects of gravity, because it is the pure optical properties of light. At Lenses made of glass or other materials, the gravity is not explained as the cause, but the deflection of light due to optical laws that have been known for centuries.
Other Arguments against the gravitational lenses
- The so-called gravitational lens effects are not visible in any galaxy or cluster of galaxies. Despite billions of galaxies, only relatively few gravitational lenses have been discovered with enormously distorted images so far.
-The lens effects occur at very distant objects. For galaxies in our cosmic neighborhood, gravitational lens effects are not visible. According to the model of gravitational lenses, however, each galaxy would cause the typical distorted lens effects.
-Even with close-ups of individual galaxies, the galaxies are shown in a distorted way. Instead of acting as a gravitational lens for objects in the sky behind it, the shown galaxies themselves are affected by the voids lens effects.
- At the telescope pictures it is possible to clearly see the voids optical lens effects on closer inspection. A galaxy or a cluster of galaxies cannot map the celestial objects gravitationally magnified in the background with the existing image sharpness.
-In contrast to the rarely observed, rather distorted lens effects which was until today thought to be caused by gravity, the Voids lenses from certain distance are available everywhere in the cosmos.
The galaxies are not located where they are seen
This phenomenon has been known for some telescope images and has also been described as a consequence of gravitational lenses. But the more we look into the space, the stronger this effect occurs to a similar shape. Because of the voids-lens effects, we do see Phantom galaxies in the wrong positions.
Not only in highly stylized, typical lens effects, but in the entire cosmos the images of the galaxies are shown in the wrong positions. The further we look into the cosmos, the more optical illusions are shown by the telescopic images.
In real, the galaxies do look different
Through the Void-lens effects, the galaxies in telescope images are mapped in a distorted way. They have irregular shapes and in the pictures one rather sees galaxy fragments than complete galaxies. Through the Void-lens effects irregular galaxy fragments are caused and those photos- until today- have been incorrectly interpreted as galaxies in their formation.
Many images of galaxy-collisions are a result of lens effects and these are optical illusions because in real these are two galaxies in distances.
There are less Galaxies as seen in the Figures
When looking into the distant regions of the universe, the objects in the pictures only are a few fragments of galaxies. Through the lens effects, galaxies are optically split into thousands of pieces and they can be seen in a distributed way over the entire image area. Not only complete multiple images of distant galaxies are visible, but the galaxies are also mapped in differently distorted ways.
Galaxy Clusters as optical Illusion
Through the Void-lens effects galaxies that are far apart from each other may appear as clusters of galaxies. Just as it can be seen on the phantom galaxies in the telescope images, clusters of phantom galaxies can also be caused by lens effects.
Figure 14: Optical illusion of a galaxy cluster, which were caused by voids lenses.
The understanding of the causes of lens effects has far-reaching consequences for astronomy. With our telescopes we see the universe through different sized "hollow glass spheres," which consist of differently sized voids. As a kind of "cosmic censorship" we therefore cannot achieve a look into the distant regions of the universe.
On my website, you can see pictures of telescopes that I have optically analyzed with the help of a simple drawing program. I will first summarize my analysis results briefly below. When viewing the telescope images, the following arguments can be better understood.
There are no gravitational lenses but only voids lenses
The amplification, attenuation, and distortion of the astronomical images, which takes place through the deflection of light beams so far has been explained as a result of gravity. It is the ordinary optical properties of light in the transition to another medium. For the explanation of astronomical lenses you do not need the effects of gravity, because it is the pure optical properties of light. At Lenses made of glass or other materials, the gravity is not explained as the cause, but the deflection of light due to optical laws that have been known for centuries.
Other Arguments against the gravitational lenses
- The so-called gravitational lens effects are not visible in any galaxy or cluster of galaxies. Despite billions of galaxies, only relatively few gravitational lenses have been discovered with enormously distorted images so far.
-The lens effects occur at very distant objects. For galaxies in our cosmic neighborhood, gravitational lens effects are not visible. According to the model of gravitational lenses, however, each galaxy would cause the typical distorted lens effects.
-Even with close-ups of individual galaxies, the galaxies are shown in a distorted way. Instead of acting as a gravitational lens for objects in the sky behind it, the shown galaxies themselves are affected by the voids lens effects.
- At the telescope pictures it is possible to clearly see the voids optical lens effects on closer inspection. A galaxy or a cluster of galaxies cannot map the celestial objects gravitationally magnified in the background with the existing image sharpness.
-In contrast to the rarely observed, rather distorted lens effects which was until today thought to be caused by gravity, the Voids lenses from certain distance are available everywhere in the cosmos.
The galaxies are not located where they are seen
This phenomenon has been known for some telescope images and has also been described as a consequence of gravitational lenses. But the more we look into the space, the stronger this effect occurs to a similar shape. Because of the voids-lens effects, we do see Phantom galaxies in the wrong positions.
Not only in highly stylized, typical lens effects, but in the entire cosmos the images of the galaxies are shown in the wrong positions. The further we look into the cosmos, the more optical illusions are shown by the telescopic images.
In real, the galaxies do look different
Through the Void-lens effects, the galaxies in telescope images are mapped in a distorted way. They have irregular shapes and in the pictures one rather sees galaxy fragments than complete galaxies. Through the Void-lens effects irregular galaxy fragments are caused and those photos- until today- have been incorrectly interpreted as galaxies in their formation.
Many images of galaxy-collisions are a result of lens effects and these are optical illusions because in real these are two galaxies in distances.
There are less Galaxies as seen in the Figures
When looking into the distant regions of the universe, the objects in the pictures only are a few fragments of galaxies. Through the lens effects, galaxies are optically split into thousands of pieces and they can be seen in a distributed way over the entire image area. Not only complete multiple images of distant galaxies are visible, but the galaxies are also mapped in differently distorted ways.
Galaxy Clusters as optical Illusion
Through the Void-lens effects galaxies that are far apart from each other may appear as clusters of galaxies. Just as it can be seen on the phantom galaxies in the telescope images, clusters of phantom galaxies can also be caused by lens effects.
Figure 14: Optical illusion of a galaxy cluster, which were caused by voids lenses.
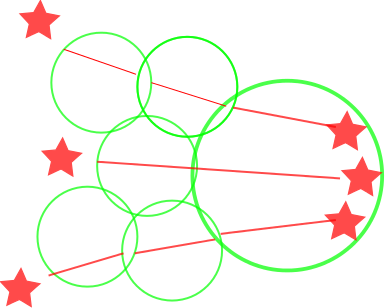
Figure 15: The most distant galaxies. According to astronomers, the marked objects are galaxies, however, these are only fragments of galaxies.
Figure 16: Here, the figures marked at the top of the picture supposedly are galaxies in a far distance. These Galaxy fragments are also caused by the complex Voids-Lens effects.
Summary
From a certain distance, we always have to consider the optical effects of natural Voids lenses in the telescopic images (I guess from about 10 light-years).
We can better examine the invisible parts of the universe, the so-called dark matter and dark energy with the analysis of the natural lens effects.
With the Void-lens effects, we can gain new insights into the cosmos from the fascinating telescopic images.
4. The Telescopic images on this website
In order to exclude systematic and technical sources of errors, such as lens aberrations or software artifacts, I have examined several pictures of different telescopes (including Amateurastronomers). The Voids-lenses are not only a ubiquitous phenomenon in the optical spectrum, but also outside the visible spectrum of electromagnetic waves.
For further analysis, I recommend the free drawing program Inkspace, with which I have drawn the circles in the telescopic images.
Here are some recent publications on similar topics (as of January 2014):
Kosmischer BOSS (German)
http://www.pro-physik.de/details/news/5721731/Kosmischer_BOSS.html
Hubblecast 70: Peering around cosmic corners
http://www.spacetelescope.org/videos/hubblecast70a/
Huge cosmic voids could probe dark energy
http://www.newscientist.com/article/dn24828-huge-cosmic-voids-could-probe-dark-energy.html#.Utq-uo0wdjo
Press Conferences from AAS 223 (American Astronomical Society), Washington D.C., 5-9 January 2014
Celestial Soundings with the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
http://aas.org/media-press/archived-aas-press-conference-webcasts
First measurement of gravitational lensing by cosmic voids in SDSS
http://arxiv.org/abs/1309.2045
THE WEIGHT OF EMPTINESS: THE GRAVITATIONAL LENSING SIGNAL OF STACKED VOIDS
http://iopscience.iop.org/2041-8205/762/2/L20/article
A Simple Gravitational Lens Model For Cosmic Voids
http://arxiv-web3.library.cornell.edu/abs/1310.7574v1
From a certain distance, we always have to consider the optical effects of natural Voids lenses in the telescopic images (I guess from about 10 light-years).
We can better examine the invisible parts of the universe, the so-called dark matter and dark energy with the analysis of the natural lens effects.
With the Void-lens effects, we can gain new insights into the cosmos from the fascinating telescopic images.
4. The Telescopic images on this website
In order to exclude systematic and technical sources of errors, such as lens aberrations or software artifacts, I have examined several pictures of different telescopes (including Amateurastronomers). The Voids-lenses are not only a ubiquitous phenomenon in the optical spectrum, but also outside the visible spectrum of electromagnetic waves.
For further analysis, I recommend the free drawing program Inkspace, with which I have drawn the circles in the telescopic images.
Here are some recent publications on similar topics (as of January 2014):
Kosmischer BOSS (German)
http://www.pro-physik.de/details/news/5721731/Kosmischer_BOSS.html
Hubblecast 70: Peering around cosmic corners
http://www.spacetelescope.org/videos/hubblecast70a/
Huge cosmic voids could probe dark energy
http://www.newscientist.com/article/dn24828-huge-cosmic-voids-could-probe-dark-energy.html#.Utq-uo0wdjo
Press Conferences from AAS 223 (American Astronomical Society), Washington D.C., 5-9 January 2014
Celestial Soundings with the Sloan Digital Sky Survey
http://aas.org/media-press/archived-aas-press-conference-webcasts
First measurement of gravitational lensing by cosmic voids in SDSS
http://arxiv.org/abs/1309.2045
THE WEIGHT OF EMPTINESS: THE GRAVITATIONAL LENSING SIGNAL OF STACKED VOIDS
http://iopscience.iop.org/2041-8205/762/2/L20/article
A Simple Gravitational Lens Model For Cosmic Voids
http://arxiv-web3.library.cornell.edu/abs/1310.7574v1

